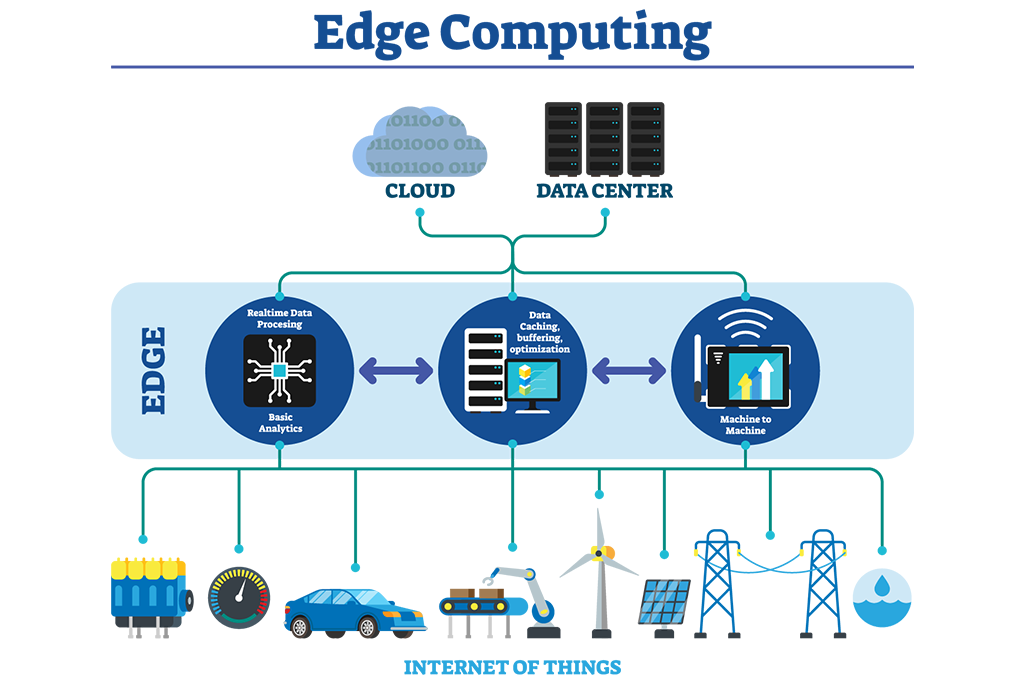
Edge computing is a distributed computing architecture that enables the processing and storage of data closer to the end-user devices and at the edge of the network. It aims to address the limitations of traditional cloud computing by reducing latency, improving responsiveness, and increasing data privacy and security. Edge computing devices, such as edge servers and gateways, can process data generated by the Internet of Things (IoT) devices, smartphones, and other connected devices in real-time, without having to send the data to the cloud.
In edge computing, data is processed and analyzed at the source, reducing the need to transfer large amounts of data over the network. This results in faster decision-making and reduces network congestion, as well as provides cost savings by reducing bandwidth and cloud storage usage.
Edge computing is becoming increasingly important for use cases that require low latency and high responsiveness, such as real-time video and audio processing, virtual reality, and autonomous vehicles. It is also useful in remote or low-connectivity areas, where sending data to the cloud is not feasible due to bandwidth limitations.
How does edge computing benefit us?
Edge computing has several benefits, including:
- Reduced Latency: By processing data at the edge of the network, edge computing reduces the time it takes to get information from the source to the user, resulting in faster and more responsive systems.
- Improved Responsiveness: Edge computing can process data in real time, making it ideal for use cases that require immediate responses, such as autonomous vehicles, virtual reality, and real-time video and audio processing.
- Increased Data Privacy and Security: Edge computing reduces the amount of data that needs to be transmitted over the network, reducing the risk of data breaches and improving privacy. Additionally, edge devices can implement security measures such as encryption, firewalls, and intrusion detection to further enhance security.
- Cost Savings: By reducing the amount of data sent to the cloud, edge computing can reduce bandwidth and cloud storage costs. Additionally, edge devices can be more cost-effective than cloud infrastructure, especially in remote or low-connectivity areas.
Overall, edge computing is a key enabler for IoT and other next-generation technologies, providing a balance between cloud and device-based computing, offering low latency and improved data privacy, security and cost-effectiveness.
For more such content, keep reading @techinnews



